
About QuestDB
QuestDB was founded in 2019 based on database technology that co-founder Vlad Ilyushchenko had been working on since 2012. The company open sourced the QuestDB project in November 2019 under the Apache 2.0 license. QuestDB was included in the Y Combinator Summer 2020 (S20) batch.
Based in London (with team members also located across the pond), the team is led by Ilyushchenko (CTO) and co-founders Tancrede Collard (CEO) and Nicolas Hourcard (CPO).
Per QuestDB, their elevator pitch is:
QuestDB is an open source SQL database designed to process time-series data, faster. QuestDB’s software architecture has been designed from the ground up to be as close to the hardware structure as possible – offering breakthrough performance. Through QuestDB, companies can harness the power of real-time and big data processing by handling billions of time-stamped events without relying on powerful hardware.
Size
- 7 employees (including the 3 founders)
- $2.3 million in funding from a seed round announced in July 2020
- Under 10 clients
- 2000+ individual users (based on downloads and other metrics)
Product and Go to Market
At present QuestDB’s focus is on 1) refining their open source database for production use cases and 2) building an active and engaged community.
QuestDB (the technology) is an open source, SQL-based database optimized for time series. The database is an append-based model designed around time series, meaning that data is appended in chronological order. Users can then run queries against data using SQL, with some additional time series functionality.
As noted in the product documentation on SQL extensions, “QuestDB attempts to implement standard ANSI SQL. We also attempt to be PostgreSQL compatible, although some of it is work in progress.” The database includes a web console consisting of a schema explorer, a code editor (for running queries), and a visualization area, which gives users the option of displaying query results in rows or, when applicable, as a bar or line graph.
Both the source code and project roap map are publicly available on GitHub. Company leadership has indicated that future direction may include a managed cloud offering aimed at the enterprise.
The company’s go to market strategy is based on developer-led bottoms up adoption (as demonstrated by making relatively early hires for developer relations). As such, it is highly motivated to get developers using the open source database, and provides installation guides and packages for Docker, Homebrew, and an installation directly from the binaries. It also leverages a Slack workspace to help with troubleshooting and to encourage community building.
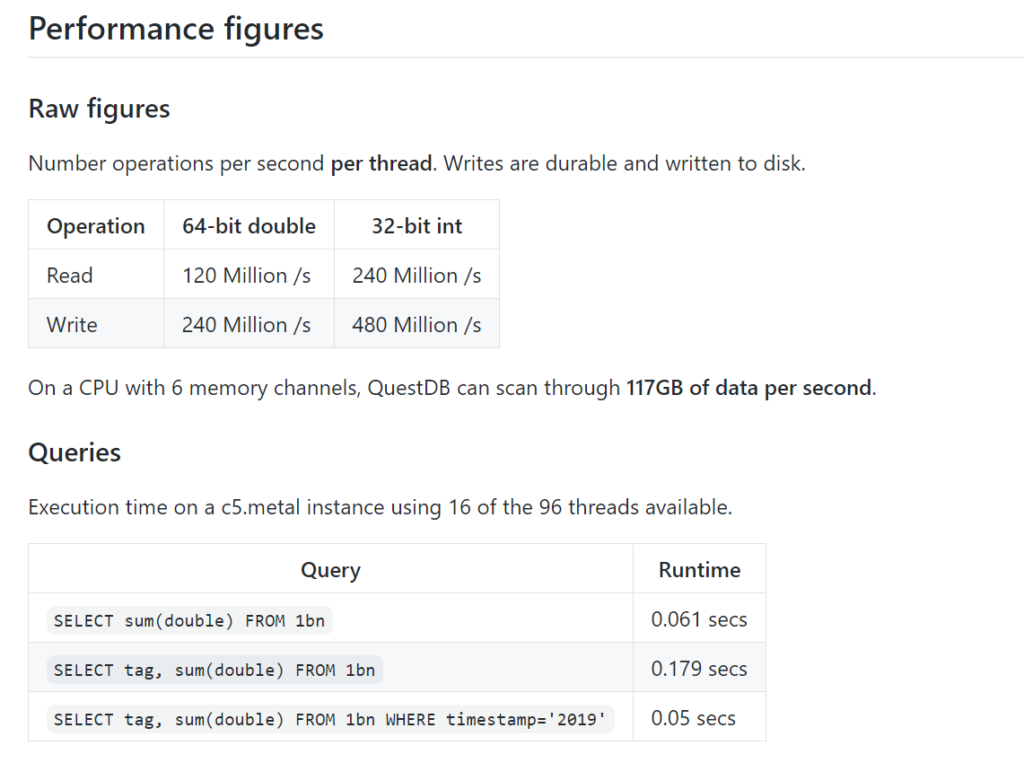
QuestDB has made a live demo of the database available at http://try.questdb.io:9000/. In keeping with its developer-led adoption aims, the company initially promoted the demo on Hacker News, then followed up with a blog post as a public review of the demo promotion. Its official Launch HN post (a Hacker News “launch” is part of what Y Combinator offers companies accepted into its startup accelerator program) narrated Ilyushchenko’s path to creating the database, but then also included a lot of developer-friendly details on query performance improvement, once again encouraging readers to try the database out for themselves. Performance figures are also posted directly on the project’s readme file.
Competitive Landscape
As indicated above, QuestDB emphasizes performance in its positioning, as it sees speed as one of its key differentiators from its competitors. QuestDB competes with database technologies such as InfluxDB, TimescaleDB, kdb+, and Clickhouse. QuestDB also hopes to attract users through simplified on-boarding, using a standard SQL syntax that is a lower barrier of entry for developers. They are also working to make data ingestion easy through their connectors and integrations.
Disclosure: QuestDB is a RedMonk client, but this is an independent piece of research that has not been commissioned by the client.

No Comments